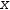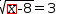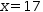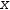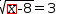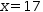3.5.5 Isolate
For an active expression that is an equation, this action applies a series of transformations that result in
the subject appearing by itself on one side of the equation.
The transformations are limited to operators and transcendental functions with
well-defined inverses.
For example, with 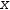 x selected in
x selected in 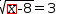 √(.{x}-8)=3, Isolate produces
√(.{x}-8)=3, Isolate produces 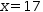 x=17.
x=17.